허프만 부호화 알고리즘
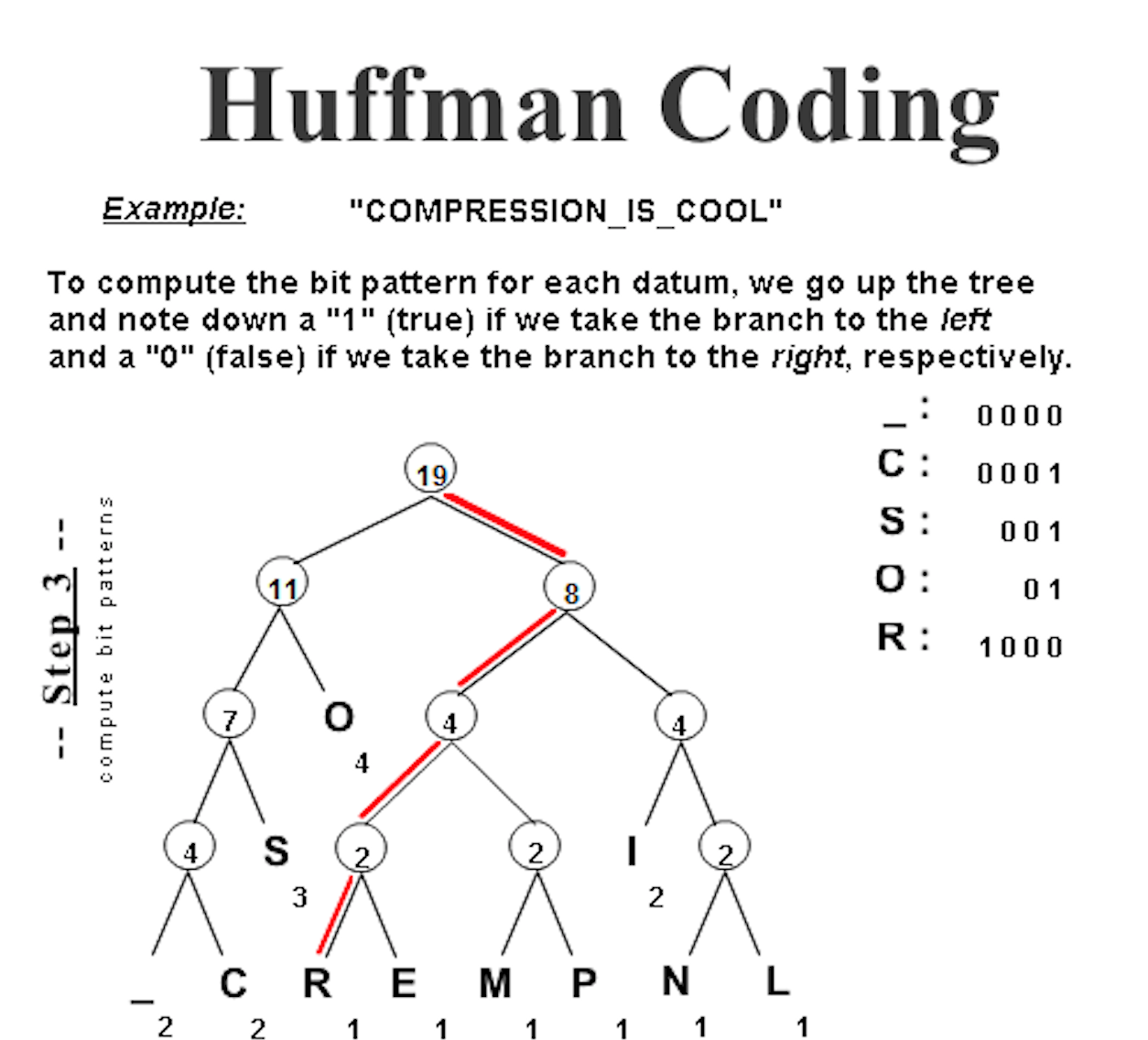
허프만 부호화 알고리즘을 추가하였습니다. uncategorized 알고리즘으로 추가하였고, 패러다임으로 구분할 때는 Greedy 알고리즘으로 추가됩니다.
기능(function)
기능으로는 encode와 decode를 추가하였습니다.
encode를 통해 문자를 부호화하고, decode를 통해 부호화된 것을 다시 원래의 문자열로 돌려 놓을 수 있습니다.
참조(References)
ReadMe 파일
Huffman Coding

In computer science and information theory, a Huffman code is a particular type of optimal prefix code that is commonly used for lossless data compression. The process of finding and/or using such a code proceeds by means of Huffman coding, an algorithm developed by David A. Huffman while he was a Sc.D. student at MIT, and published in the 1952 paper “A Method for the Construction of Minimum-Redundancy Codes”.
The output from Huffman’s algorithm can be viewed as a variable-length code table for encoding a source symbol (such as a character in a file). The algorithm derives this table from the estimated probability or frequency of occurrence (weight) for each possible value of the source symbol. As in other entropy encoding methods, more common symbols are generally represented using fewer bits than less common symbols. Huffman’s method can be efficiently implemented, finding a code in time linear to the number of input weights if these weights are sorted.
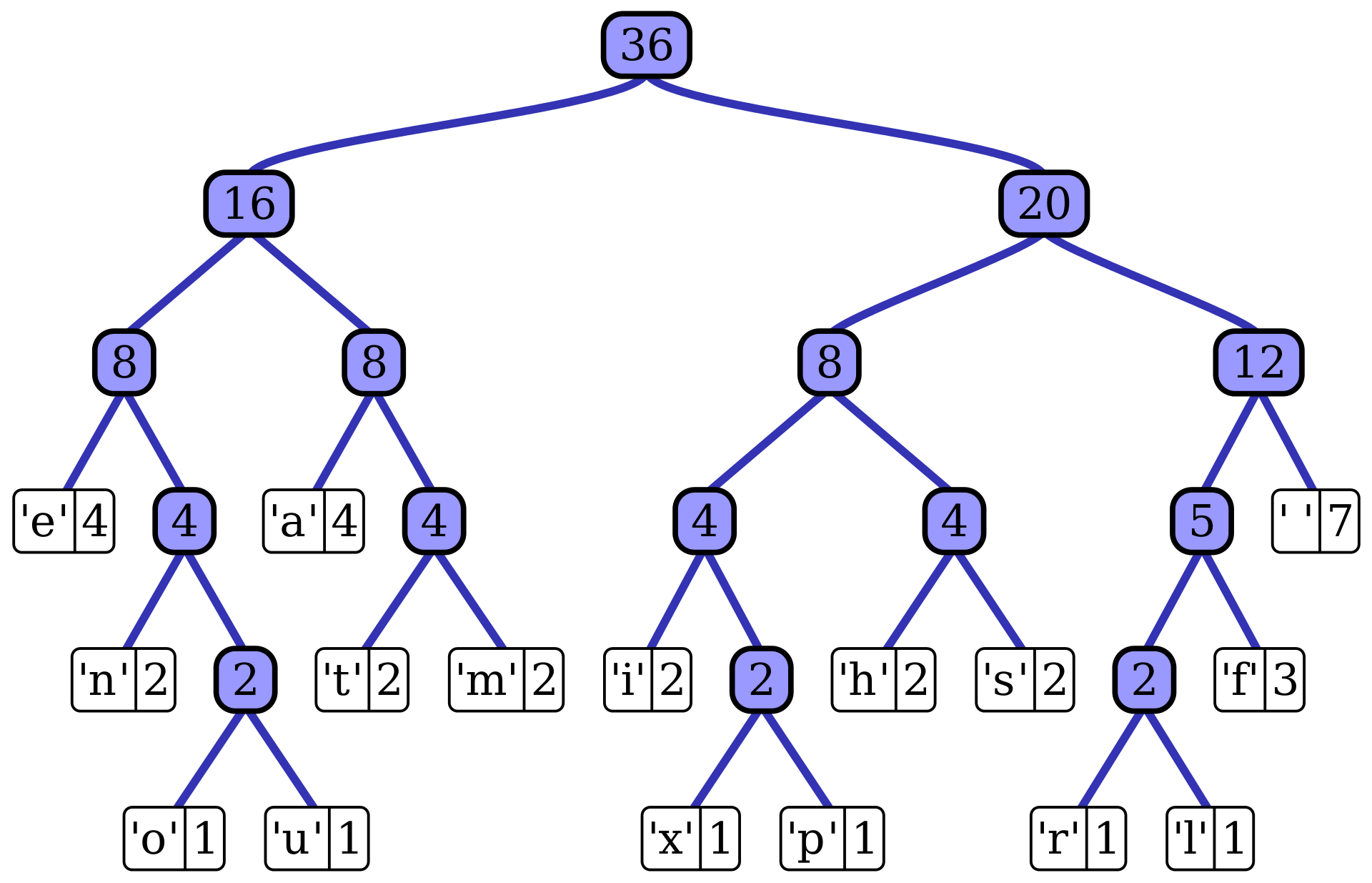
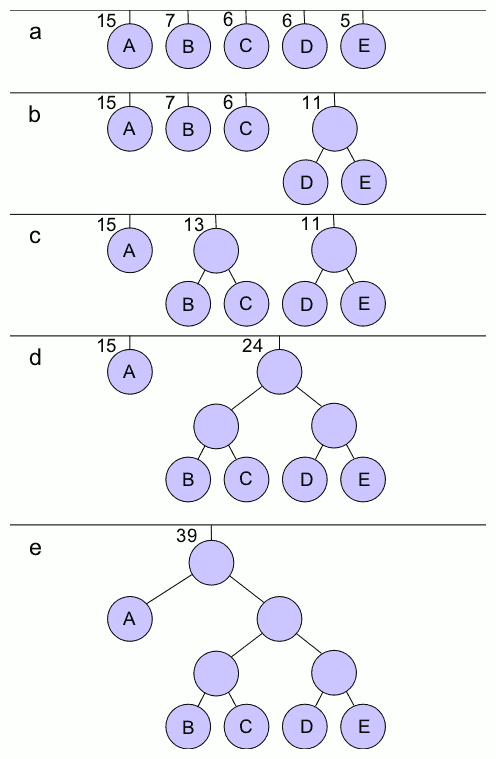
Constructing a Huffman Tree
Encode : Compression

The simplest construction algorithm uses a priority queue where the node with lowest probability is given highest priority:
- Create a leaf node for each symbol and add it to the priority queue.
- While there is more than one node in the queue:
- Remove the two nodes of highest priority (lowest probability) from the queue
- Create a new internal node with these two nodes as children and with probability equal to the sum of the two nodes’ probabilities.
- Add the new node to the queue.
- The remaining node is the root node and the tree is complete.
Since efficient priority queue data structures require
O(log n)time per insertion, and a tree withnleaves has2n−1nodes, this algorithm operates inO(n log n)time, wherenis the number of symbols.